➤ Defined in many different ways, but not rigorously.
- A decision support database that is maintained separately from the organization’s operational database.
- A consistent database source that bring together information from multiple sources for decision support queries.
- Support information processing by providing a solid platform of consolidated, historical data for analysis.
History of Data Warehousing
➤ In the 1990’s executives became less concerned with the day-to-day business operations and more concerned with overall business functions.
➤ The data warehouse provided the ability to support decision making without disrupting the day-to-day operations, because :
- Operational information is mainly current – does not include the history for better decision making
- Issues of quality information
- Without information history, it is difficult to tell how and why things change over time
Data Warehouse Fundamentals
➤ Data warehouse – A logical collection of information – gathered from many different operational databases – that supports business analysis activities and decision-making tasks.
➤The primary purpose of a data warehouse is to combined information throughout an organization into a single repository for decision-making purposes – data warehouse support only analytical processing.
Data Warehouse Model
➤ Extraction, transformation and loading (ETL) – A process that extracts information from internal and external databases, transforms the information using a common set of enterprise definitions, and loads the information into a data warehouse.
➤ Data warehouse then send subsets of the information to data mart.
➤ Data mart – contains a subset of data warehouse information.

Multidimensional Analysis and Data Mining
➤ Relational Database contains information in a series of two-dimensional tables.
➤ In a data warehouse and data mart, information is multidimensional, it contains layers of columns and rows.
Dimension – A particular attribute of information.
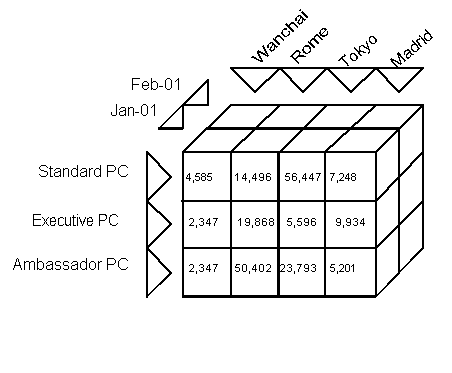
Cube – Common term for the representation of multidimensional information.
➤ Once a cube of information is created, users can begin to slice and dice the cube to drill down into the information.
➤ Users can analyze information in a number of different ways and with number of different dimensions.
Data Mining – the process of analyzing data to extract information not offered by the raw data alone. Also known as “knowledge discovery” – computer-assisted tools and techniques for sifting through and analyzing vast data stores in order to finds trends, patterns and correlations that can guide decision making and increase understanding.
➤ To perform data mining users need data-mining tools.
Data-mining tool – uses a variety of techniques to finds patterns and relationships in large volumes of information. Eg: retailers and use knowledge of these patterns to improve the placement of items in the layout of a mail-order catalog page or Web page.
Information Cleansing or Scrubbing
➤ An organization must maintain high-quality data in the data warehouse.
➤ Information cleansing or scrubbing – A process that weeds out and fixes or discards inconsistent, incorrect or incomplete information.
➤ Occurs during ETL process and second on the information once if is in the data warehouse.
➤ Contract information in an operational system.

➤ Standardizing Customer name from Operational Systems

➤ Information cleansing activities

➤ Accurate and complete information

Business Intelligence
Business Intelligence – refers to applications and technologies that are used to gather, provides access, analyze data and information to support decision making efforts.
➤ These systems will illustrate business intelligence in the areas of customer profiling, customer support, market research, market segmentation, product profitability, statistical analysis, and inventory and distribution analysis to name a few.
➤ Eg; Excel, Access
No comments:
Post a Comment